One of the main concerns we all have about our smartphones is battery life. And for now, the solution is still in the chargers.
There are different types of fast chargers on the market with which you can recover the power of your battery more quickly. The most common are standard USB chargers with more than two amps (2A) that charge devices at a faster rate than conventional ones. Another popular alternative is Qualcomm’s Quick Charge chargers, as well as third-party solutions such as Samsung’s Adaptive Fast Charging (AFC), Huawei’s Supercharge or OnePlus Dash charge…
Another solution that probably will gain popularity is Fast Charge wireless charging based on the Qi standard. And more after announcing Apple that their new devices, iPhone X, iPhone 8, iPhone 8 Plus and Apple Watch, were going to be compatible.
As you can see, there are several alternatives that can help us to reduce the time it takes to invest in the smartphone charging process. Now let’s look at the differences between them.
What is fast charging?
The exact method by which charging is quickest may vary from system to system, but in a simplified way it is as simple as increasing the “power” so that the battery recharges faster by increasing voltage, amperage, or both.
Fast charging types
1. USB standard charging method
The good thing about the universal charging is that any device is compatible with this type of chargers. As a general rule, traditional chargers we use for mobile phones have a voltage of 5V and a current between 1 A and 2.4 A. In other words, it works at 5V and at different intensities. The higher the intensity of the charger the faster it is able to charge, but eventually it will be the charging device that determines the charge current.

Benefits of standard USB charging
As we have said, the advantage of this method is that basically all smartphone models allow charging at more than 2 A. And while chargers with more than 2 A are usually a little more expensive, they allow you to charge your device faster.
In addition, the new USB chargers are capable of charging multiple devices at the same time with their multiple USB slots and they have power enough (W) to make the charging speed the maximum allowed for each device, which means a reduced charging time.
Loading time estimation:
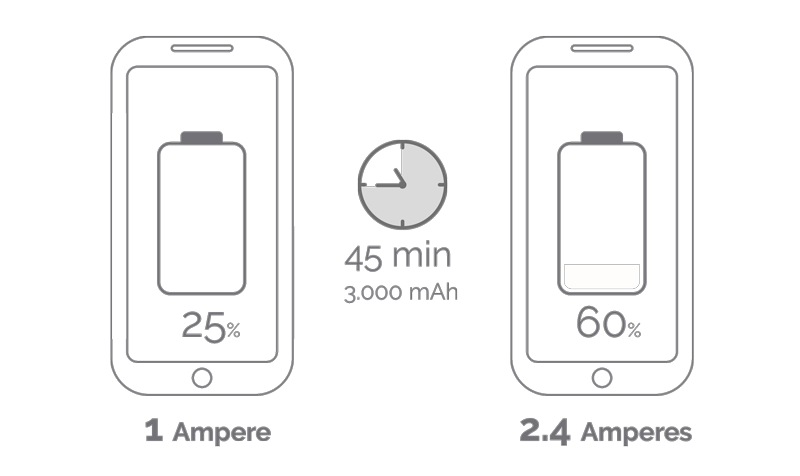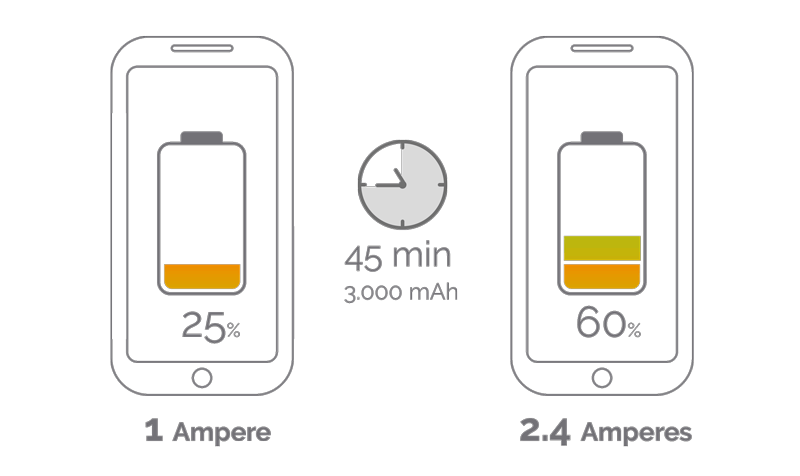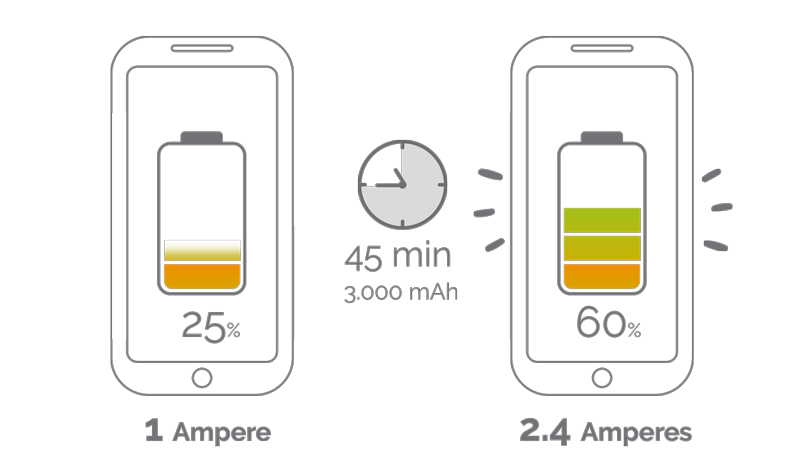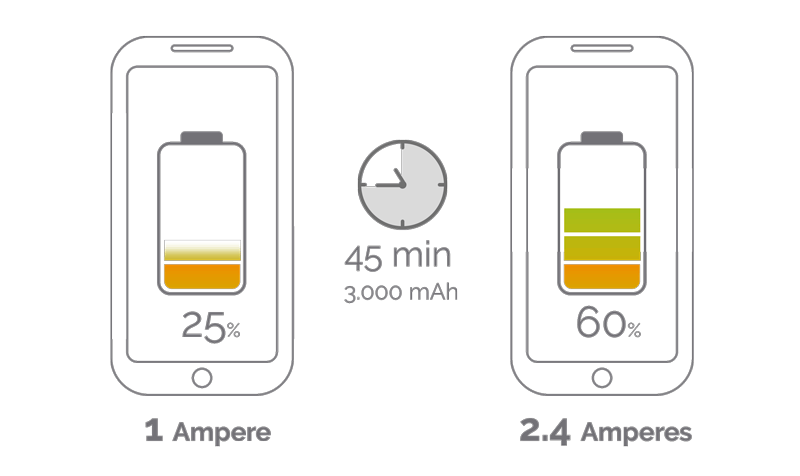
As you have seen, the difference between charging faster or slower lies in milliamps. We’re going to test a mid-range smartphone – around €200 – with a battery capacity of 3,000 mAh. How long will it take to charge?
This 3,000 mAh phone with a 1A charger will take at least 3 hours to charge. The same mobile phone with a 2.4A charger will take 1.25 hours to charge.
All this assuming a 100% efficiency, which is not real: usually efficiency is around 80% or 70%, so the times will be slightly higher.
In other words, the 2.4A charger is 58% faster than the 1A charger, a remarkable difference.
2. Qualcomm Quick Charge charging method
Quick Charge is Qualcomm’s fast loading technology associated with its processors. How does it work? A common charger on a mobile phone offers a constant voltage of 5V at 1A or 2A current, while a charger with Quick Charge 2.0 technology will provide an output of 5V, 9V and up to 12V. This is a quick charging system that saves up to 75% of the total charging time of a battery. To give you an idea: Quick Charge 2.0 technology is capable of charging 60% of a 3,300 mAh battery in 30 minutes.
The different versions of Quick Charge mix the number of voltage and amperage combinations supported by the system and incorporate different technologies for greater efficiency and safety. Thus, Quick Charge 1.0 supports 5V and 2A, Quick Charge 2.0 added 5V, 9V and 12V and 3A.
From Quick Charge 3.0 onwards the thing changes: enlarges the selection of voltages between 3.2V and 20V in 200mV increments, i. e. the load becomes dynamic, allowing the mobile device to adjust the required load voltage at all times. Quick Charge 4.0 among many other new features includes support for USB Power Delivery and the “five-five” philosophy. Five minutes charging to gain five hours of autonomy. The Quick charge 4+ version is now available, implementing 15% more speed in the load.
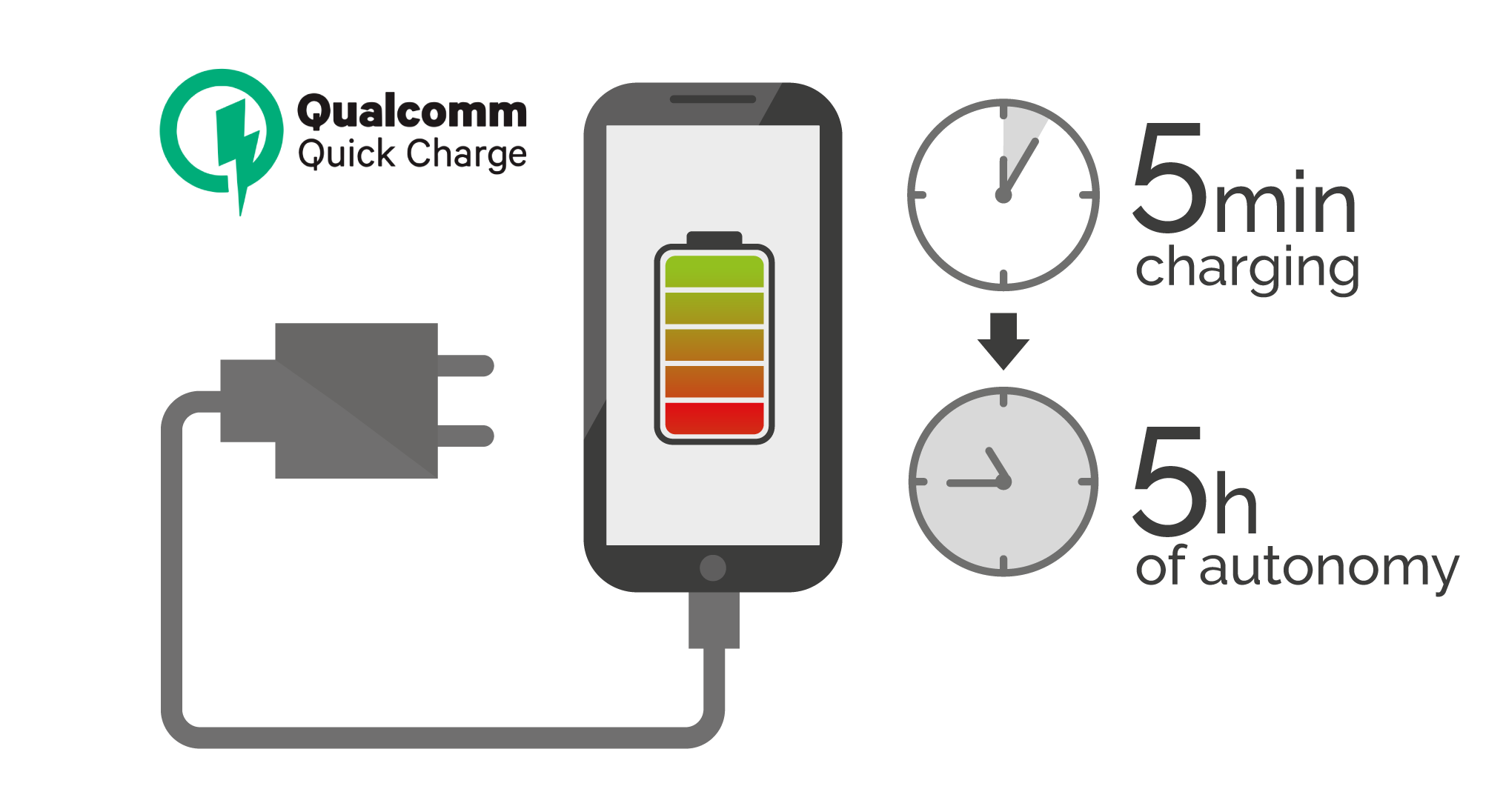
Although this type of fast charging has a basic drawback: you cannot choose and either you have a compatible mobile or you don’t have it. In order to make use of this fast charge, both the device and the charger have to support Quick Charge technology.
It should be noted that the Quick Charge 2.0 technology, the most extended version, is the same as the technology behind other quick charging systems such as Motorola TurboPower or Samsung Adaptive Fast Charge. And they’re not the only ones, other manufacturers are also betting on fast charging, such as Mediatek and its Pump Express; Huawei and its SuperCharge or Dash Charge, the fast charging technology that features the new OnePlus mobile phones.
3. Wireless charging method
Wireless charging has been around for a long time, but it’s back in fashion. And the one responsible, as it could not be otherwise, is Apple. Cupertino’s brand takes the leap and includes Qi wireless charging standard on its new phones –iPhone X, iPhone 8 and iPhone 8 Plus–. The advantage is that being compatible Apple devices compatible with the Qi standard, you can use multiple chargers and not just the Apple official.

How does wireless charging work?
Wireless charging works by inducing the charge by means of an electromagnetic field formed by a coil. Thus, the charger transfers power to the phone and charges its battery by simply placing it on the charging base. However, the charger must be connected to the electrical current.
The main drawback of wireless charging is that most chargers are not fast charging. Wireless chargers typically offer 5W power, which makes the time to reach full charge significantly longer than using a wired charger. There are still things to be polished here. And this includes manufacturers such as LG, Samsung and Lenovo, which, taking advantage of the Qi standard, have launched new wireless fast chargers.
On the market you can find Qi wireless charging models that offer fast charging speeds with up to 7.5 watts of power. That’s 40% faster than a conventional 1A charger. What’s more, the LG Quick charger offers three times the power: 15W and, according to the company itself, achieves 50% charge in just 30 minutes. At the moment they are an exception, we will have to wait and see what Apple can do for the wireless charging. We’ll see if it gives it the big boost and improves the charging speed.
Conclusion:
The idea is very simple: we want to charge the phone’s battery much faster, so that the mobile phone is connected to the power supply for as little time as possible. So you can choose the type of fast charging that’s right for you, but make sure your mobile phone supports the technology. If this is not the case, opt for universal fast charging with an extra amperage charger.